Electronic actuators are pivotal components in modern automation and control systems, transforming electrical energy into precise mechanical motion. These devices are essential in numerous applications across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, robotics, and home automation. This article delves into the fundamentals, types, applications, and future prospects of electronic actuators, highlighting their significance in today’s technologically advanced world.
What is an Electronic Actuator?
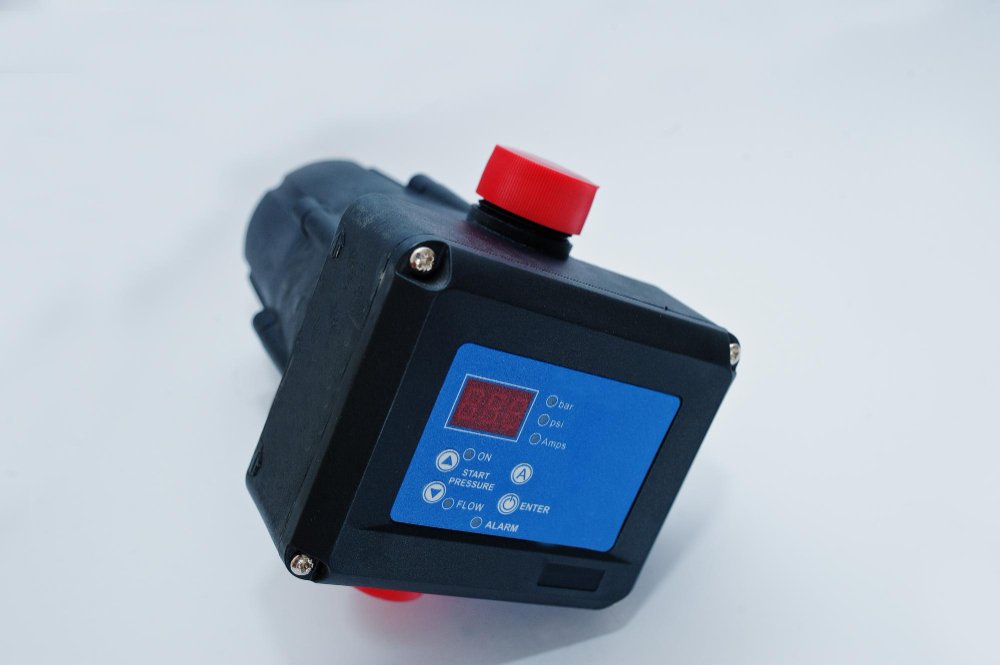
An electronic actuator is a device that converts electrical signals into physical movement. This movement can be linear, rotary, or oscillatory, depending on the actuator design and application requirements. Electronic actuators are integral to systems requiring precise control and automation, enabling enhanced efficiency and performance.

Types of Electronic Actuators
- Linear Actuators: These actuators produce linear motion, moving in a straight line. Commonly used in applications such as robotic arms, industrial machinery, and adjustable beds, linear actuators are essential for tasks requiring straightforward movement.
- Rotary Actuators: Rotary actuators provide rotational motion, ideal for applications like valve control, camera positioning systems, and motorized turntables. They are crucial in systems where angular displacement is necessary.
- Piezoelectric Actuators: Utilizing the piezoelectric effect, these actuators produce small, precise movements by applying voltage to piezoelectric materials. They are used in applications requiring ultra-fine adjustments, such as in optical devices and precision engineering.
- Electrohydraulic Actuators: Combining electric and hydraulic mechanisms, these actuators are suitable for high-force applications. They are often found in heavy machinery, aircraft control surfaces, and industrial automation systems.
- Electromagnetic Actuators: These actuators employ electromagnetic fields to generate motion. Solenoids, a type of electromagnetic actuator, are widely used in locking mechanisms, relays, and automotive systems.
Applications of Electronic Actuators
- Automotive Industry: Electronic actuators are fundamental in modern vehicles, controlling various functions such as throttle position, fuel injection, and brake systems. They enhance vehicle performance, safety, and fuel efficiency.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace sector, actuators are used in flight control systems, landing gear, and cargo handling. Their reliability and precision are critical for the safety and performance of aircraft.
- Robotics: Robotic systems rely heavily on actuators for movement and manipulation. From industrial robots performing assembly line tasks to medical robots conducting surgeries, actuators are the backbone of robotic functionality.
- Home Automation: Electronic actuators play a significant role in smart home devices, including motorized window blinds, adjustable furniture, and automated door locks. They contribute to the convenience and efficiency of modern living spaces.
- Industrial Automation: In manufacturing and production environments, actuators are used in automated assembly lines, conveyor systems, and packaging machinery. They enable high precision, speed, and consistency in industrial processes.
Advantages of Electronic Actuators
- Precision: Electronic actuators offer high accuracy in positioning and movement, essential for applications requiring exact control.
- Efficiency: They are energy-efficient, converting electrical energy directly into mechanical work with minimal losses.
- Reliability: With fewer moving parts compared to hydraulic or pneumatic systems, electronic actuators have lower maintenance requirements and longer operational lifespans.
- Integration: Easy integration with electronic control systems allows for advanced automation and remote control capabilities.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While electronic actuators present numerous benefits, they also face challenges such as susceptibility to electromagnetic interference and the need for robust electronic control systems. However, ongoing advancements in materials science, sensor technology, and control algorithms are continually enhancing actuator performance.
The future of electronic actuators is promising, with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) paving the way for smarter, more adaptive actuator systems. These advancements will lead to even greater efficiency, precision, and versatility, further cementing the role of electronic actuators in the automation landscape.

Conclusion
Electronic actuators are integral to the functionality and advancement of modern technology. Their ability to precisely control mechanical movement in response to electrical signals makes them indispensable in various industries. As technology continues to evolve, electronic actuators will undoubtedly play a critical role in shaping the future of automation and control systems, driving innovation and efficiency across countless applications.