Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition caused by blood clots forming in the deep veins, usually in the legs. While it might sound alarming, being aware of the symptoms and risk factors can help you catch it early and seek timely medical intervention. This article aims to educate you about DVT symptoms, how they develop, and why early detection is crucial.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis is a medical condition in which blood clots form in the veins located deep within your body. Most commonly, these clots appear in the legs but can occur in other parts of the body. If left untreated, DVT can lead to severe complications such as pulmonary embolism, where a clot travels to the lungs, potentially becoming life-threatening.
Recognizing DVT Symptoms
The key to managing DVT effectively is identifying its symptoms early. Here are the most common signs you should watch out for:
-
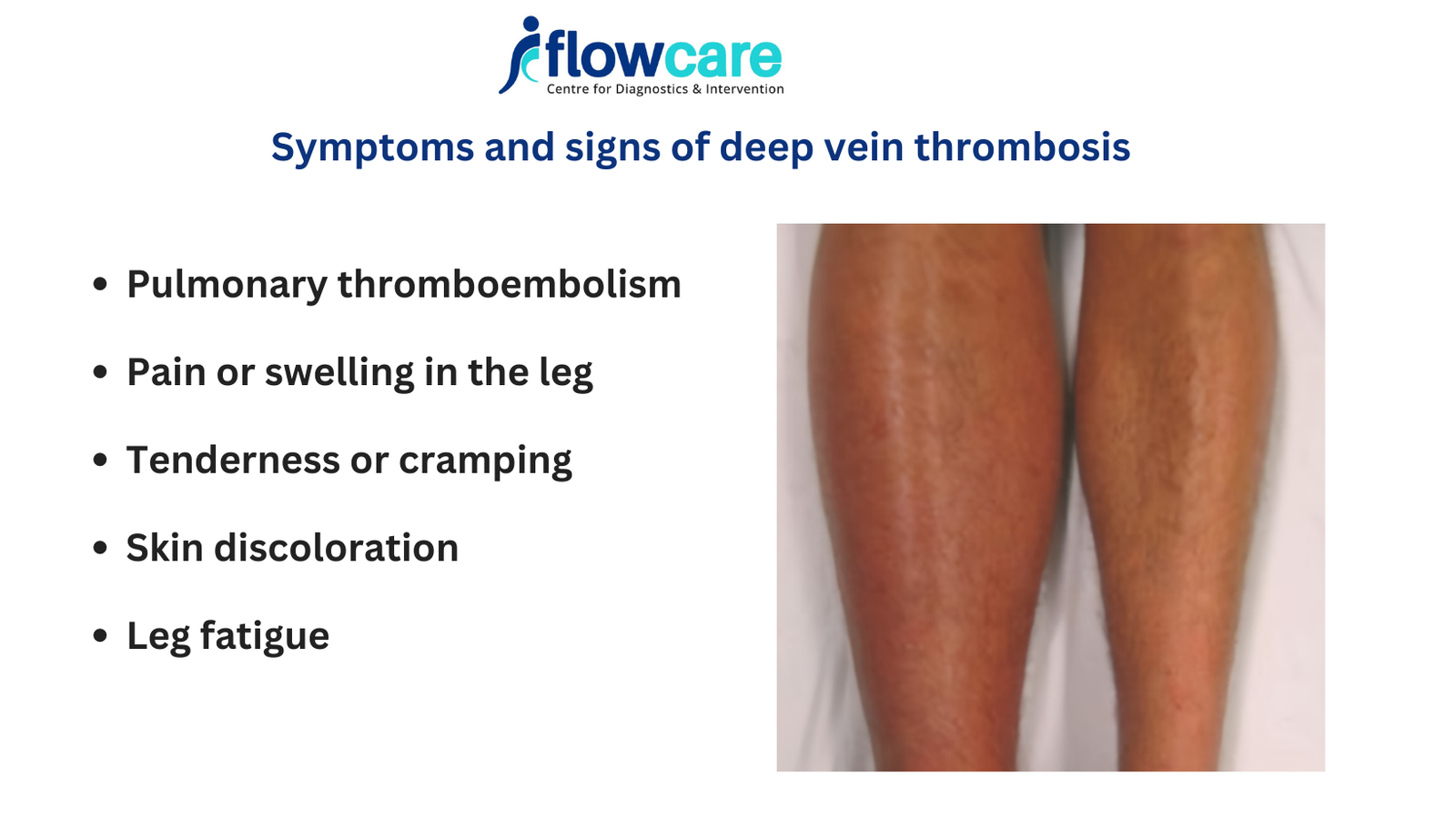
Swelling in the Affected Limb
- Sudden or gradual swelling in one leg is a common DVT symptom. The swelling may feel uncomfortable or tight.
-
Pain or Tenderness
- Pain, often described as cramping or soreness, usually starts in the calf and may intensify over time.
-
Red or Discolored Skin
- The skin around the affected area may turn reddish or purple and feel warm to the touch.
-
Enlarged Veins
- Veins near the surface of the skin may appear more prominent and feel tender.
-
Difficulty Walking
- Discomfort or heaviness in the leg can make walking or standing for long periods challenging.
If you notice one or more of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional immediately for proper evaluation and treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
Certain factors increase your risk of developing DVT. Being aware of these can help you take preventive measures:
-
Prolonged Immobility
- Sitting for long periods, such as during flights or car rides, can slow blood flow and increase clotting risks.
-
Surgery or Injury
- Recent surgeries, particularly orthopedic ones, can lead to temporary blood flow disruptions.
-
Medical Conditions
- Conditions such as cancer, heart disease, or clotting disorders can raise DVT risks.
-
Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to DVT development.
-
Pregnancy and Birth Control Pills
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy or due to contraceptive pills can alter blood flow and clotting tendencies.
Diagnosing DVT
Early diagnosis of DVT is critical. If you experience symptoms, your doctor may recommend:
-
Ultrasound
- A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to detect clots in veins.
-
Blood Tests
- Tests like D-dimer levels can indicate abnormal clotting activity.
-
Imaging Scans
- In some cases, a CT or MRI scan may be necessary for a detailed view of the veins.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, several treatment approaches can help manage DVT:
-
Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners)
- These medications reduce clotting and prevent new clots from forming.
-
Compression Stockings
- Wearing these can improve blood flow and reduce swelling.
-
Thrombolytic Therapy
- In severe cases, clot-dissolving medications may be administered.
-
Surgical Intervention
- Rarely, surgery might be needed to remove the clot or place a filter in the vein.
Preventing DVT
Preventing DVT is often easier than treating it. Here are practical steps to lower your risk:
-
Stay Active
- Regular exercise improves blood circulation and prevents stagnation.
-
Avoid Prolonged Sitting
- Take breaks during long flights or car rides to stretch your legs.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight
- A balanced diet and weight management reduce stress on your veins.
-
Quit Smoking
- Smoking cessation significantly decreases clotting risks.
-
Wear Compression Gear
- Use compression socks during long trips or as advised by your doctor.
When to Seek Medical Help
DVT symptoms can range from mild to severe. However, if you experience any of the following, seek medical attention immediately:
- Sudden chest pain or difficulty breathing (could indicate pulmonary embolism).
- Swelling or pain that worsens rapidly.
- Any signs of infection like fever or redness at the affected site.
Conclusion
Being informed about DVT symptoms and understanding the risks can make a significant difference in prevention and treatment. If you suspect you might have DVT, don’t delay consulting a healthcare professional. Early detection saves lives and prevents complications like pulmonary embolism.
Taking proactive steps such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and staying aware of your body’s signals can go a long way in keeping DVT at bay. Stay vigilant, and prioritize your health.