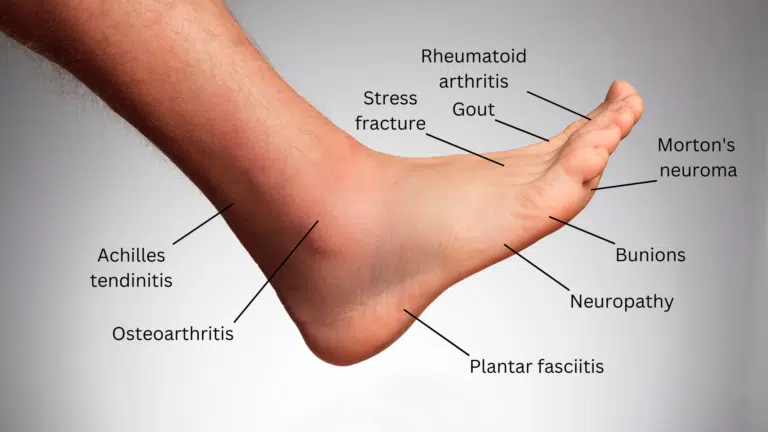
Top foot pain can be a frustrating and debilitating issue for many people. It can affect your ability to walk, exercise, or even complete everyday tasks. While top foot pain can affect anyone, certain groups of individuals are at a higher risk. Understanding these risk factors can help in identifying the cause and seeking timely treatment to alleviate pain and prevent further complications.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the factors that make some individuals more prone to developing pain on the top of the foot, common conditions associated with this issue, and actionable tips for prevention and management. We’ll also touch upon how a top foot pain chart can assist in pinpointing the cause of your discomfort.
1. Athletes and Sports Enthusiasts
Why They Are at Risk:
Athletes, particularly runners, dancers, and soccer players, are at high risk for developing top foot pain. The repetitive stress placed on the feet during sports can lead to overuse injuries, such as stress fractures or extensor tendonitis.
High-impact activities place strain on the tendons, bones, and muscles, which may lead to inflammation and pain on the top of the foot. Wearing improper footwear during sports or overtraining without adequate rest increases the likelihood of injury.
How to Manage and Prevent:
- Invest in high-quality, well-cushioned sports shoes.
- Include cross-training in your exercise routine to avoid overuse injuries.
- Stretch and strengthen foot muscles regularly to improve resilience.
2. People with High Arches or Flat Feet
Why They Are at Risk:
Structural abnormalities in the foot, such as high arches or flat feet, can place uneven pressure on different parts of the foot, including the top. This imbalance may lead to pain, particularly when walking, standing for long periods, or engaging in physical activities.
High arches often make the foot less flexible, while flat feet may strain ligaments and tendons, causing discomfort.
How to Manage and Prevent:
- Use custom orthotics to provide support and redistribute pressure.
- Choose shoes that accommodate your foot type.
- Avoid prolonged periods of standing or walking without adequate breaks.
3. Older Adults
Why They Are at Risk:
As we age, the natural cushioning in our feet diminishes, and bones become more brittle. Older adults are more susceptible to conditions such as arthritis, which can cause pain and stiffness in the top of the foot. Degenerative changes in the joints, tendons, and ligaments also contribute to discomfort.
How to Manage and Prevent:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on your feet.
- Stay active with low-impact exercises like swimming or yoga.
- Consult a foot specialist to manage age-related conditions.
4. People with Occupations That Require Prolonged Standing
Why They Are at Risk:
Jobs that demand long hours of standing or walking, such as retail workers, healthcare providers, and construction workers, increase the risk of developing foot pain. Continuous pressure on the feet can lead to fatigue, inflammation, and pain in various areas, including the top of the foot.
How to Manage and Prevent:
- Wear supportive shoes with cushioning and arch support.
- Use anti-fatigue mats if standing for extended periods.
- Take breaks to rest and elevate your feet whenever possible.
5. Individuals with Pre-existing Medical Conditions
Why They Are at Risk:
Certain medical conditions make individuals more prone to top foot pain. For example:
- Diabetes: Neuropathy and poor circulation can lead to foot pain and increase the risk of complications.
- Gout: This form of arthritis causes sudden and severe pain, often in the top of the foot.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons due to repetitive stress can cause localized pain.
How to Manage and Prevent:
- Monitor and manage underlying medical conditions.
- Stay hydrated and follow a balanced diet to reduce inflammation.
- Visit a podiatrist regularly for preventive care.
6. Women Who Frequently Wear High Heels
Why They Are at Risk:
Wearing high heels places the foot in an unnatural position, causing strain on the tendons and joints in the top of the foot. Over time, this can lead to chronic pain and even structural deformities like bunions or hammertoes.
How to Manage and Prevent:
- Limit the amount of time spent in high heels.
- Opt for shoes with a wider toe box and lower heels.
- Stretch your feet and calves regularly to improve flexibility.
7. Individuals Recovering from Foot Injuries
Why They Are at Risk:
Recovering from a foot injury, such as a fracture or sprain, increases susceptibility to pain in the top of the foot. This may be due to compensatory movements or incomplete healing. Returning to physical activity too soon can exacerbate the issue.
How to Manage and Prevent:
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for rehabilitation.
- Gradually reintroduce weight-bearing activities.
- Use supportive footwear or braces as needed during recovery.
8. People with Poor Footwear Choices
Why They Are at Risk:
Ill-fitting or unsupportive shoes are a common cause of top foot pain. Shoes that are too tight can compress the top of the foot, while those with insufficient arch support or cushioning fail to protect against impact and strain.
How to Manage and Prevent:
- Always try on shoes and walk around to test comfort before purchasing.
- Replace worn-out shoes to maintain proper support.
- Avoid narrow or overly restrictive footwear.
9. Overweight or Obese Individuals
Why They Are at Risk:
Excess body weight places additional pressure on the feet, leading to strain on the bones, ligaments, and tendons. Over time, this can result in chronic foot pain, including pain in the top of the foot.
How to Manage and Prevent:
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Use orthotic inserts to provide additional support.
- Wear shoes designed to accommodate higher weight loads.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience persistent top foot pain, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. A podiatrist can perform a thorough evaluation, including imaging tests if necessary, to determine the underlying cause. Using a top foot pain chart, a specialist can pinpoint specific areas of discomfort and provide a tailored treatment plan.
Early intervention is crucial to prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery.
Conclusion
Top foot pain can stem from a variety of factors, ranging from lifestyle choices to underlying medical conditions. By understanding who is most at risk and why, you can take proactive steps to protect your feet and minimize discomfort.
Whether it’s choosing the right footwear, managing weight, or seeking expert care, addressing the root cause is key to maintaining foot health.