Introduction
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are revolutionizing the gaming industry by providing unprecedented levels of immersion, interaction, and realism. AR enhances real-world environments with digital overlays, as seen in games like Pokémon GO, creating engaging and socially interactive experiences. Meanwhile, VR transports players into entirely virtual worlds, exemplified by titles such as Beat Saber and Half-Life: Alyx, where players can interact with their surroundings in a highly intuitive and physically engaging manner. Together, these technologies are not only redefining gameplay mechanics and user interfaces but also expanding the possibilities for game design, storytelling, and cross-platform integration, promising a dynamic and transformative future for gaming.
Definition
Through the use of devices like smartphones or glasses, augmented reality (AR) superimposes digital data on the physical world, improving the user’s view. With the use of virtual reality (VR), users can engage with realistic digital settings that imitate the real world, usually through the use of headgear. In addition to improving real-world situations, these technologies take users to fully virtual worlds, providing distinctive experiences.
Here’s an overview of how AR and VR are transforming gaming:
Augmented Reality (AR)
Enhanced Real-World Interaction:
Pokémon GO: This game is a prime example of AR’s potential, overlaying virtual creatures onto real-world locations using GPS and smartphone cameras. It encourages players to explore their surroundings to capture Pokémon, blending the virtual and physical worlds.
Minecraft Earth: This AR version of Minecraft allows players to build structures in the real world, visible through their devices, fostering creativity and collaboration in a real-world context.
Social Gaming:
AR games often involve social components where players meet and interact in the real world. This can lead to community building and shared experiences that traditional gaming might not offer.
Enhanced User Interface (UI):
AR can create dynamic and context-sensitive UIs that adapt based on the player’s real-world environment, providing a more intuitive and seamless gaming experience.
Virtual Reality (VR)
Immersive Experiences:
Beat Saber: This rhythm-based game places players in a virtual environment where they slash blocks to the beat of the music. The fully immersive VR experience makes it highly engaging and physically interactive.
Half-Life: Alyx: This VR game has set a new standard for VR gaming with its detailed environments, intricate gameplay mechanics, and deep narrative, showcasing the potential for immersive storytelling in VR.
New Gameplay Mechanics:
VR introduces unique gameplay mechanics that are not possible with traditional gaming setups. This includes full-body movement, hand tracking, and spatial awareness, allowing for more interactive and physically engaging games.
Simulation and Training:
VR is used for realistic simulation and training games. Flight simulators, driving games, and sports training applications offer players a highly realistic experience, often used for both entertainment and professional training purposes.
Cross-Platform Integration
Mixed Reality (MR):
Some games are beginning to explore mixed reality, where AR and VR elements are combined. This allows for seamless transitions between real and virtual worlds, creating a cohesive gaming experience.
Cross-Device Play:
Many AR and VR games support cross-platform play, enabling players on different devices (such as VR headsets, smartphones, and PCs) to interact within the same game environment.
Expansion in Enterprise Applications:
Beyond gaming and entertainment, AR and VR are gaining traction in enterprise applications. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and retail are leveraging these technologies for training, remote collaboration, and enhanced customer experiences. Companies are investing in immersive solutions to improve productivity and engagement.
Advancements in AR and VR Hardware:
The development of lighter, more powerful headsets with better resolution and improved user comfort is accelerating adoption. Wireless AR and VR devices with enhanced battery life and processing power will further drive their use in both consumer and enterprise sectors.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence:
AI-powered AR and VR solutions are becoming more sophisticated, offering enhanced personalization, real-time object recognition, and interactive experiences. This integration will enable more intuitive user interactions, improving usability across applications such as virtual shopping and remote learning.
5G and Edge Computing Enhancements:
Faster data speeds and lower latency with 5G networks will significantly improve AR and VR experiences. Combined with edge computing, these technologies will allow seamless processing of large-scale virtual content, reducing the dependence on heavy hardware and improving real-time responsiveness.
Growth in the Metaverse:
The concept of the metaverse is expanding, with AR and VR playing a crucial role in creating immersive digital spaces. Businesses and consumers are exploring virtual worlds for social interactions, e-commerce, and remote work, shaping a new digital economy.
Wider Adoption in Healthcare:
AR and VR are transforming healthcare with applications in surgery simulation, mental health therapy, and patient rehabilitation. Virtual reality exposure therapy (VRET) is being used to treat anxiety disorders, while AR is assisting surgeons with real-time data overlays.
Enhanced AR for Retail and E-Commerce:
Retailers are integrating AR for virtual try-ons, 3D product visualizations, and interactive shopping experiences. As consumers seek more immersive engagement, AR-driven e-commerce is expected to grow rapidly, bridging the gap between online and in-store shopping.
Immersive Education and Training:
Educational institutions and corporate training programs are increasingly using AR and VR to create interactive learning experiences. These technologies provide hands-on training in a risk-free environment, particularly for medical, engineering, and military applications.
Greater Focus on Privacy and Ethics:
As AR and VR become more integrated into daily life, concerns over data privacy and ethical considerations are growing. Companies will need to implement robust security measures to protect user data and ensure responsible use of immersive technologies.
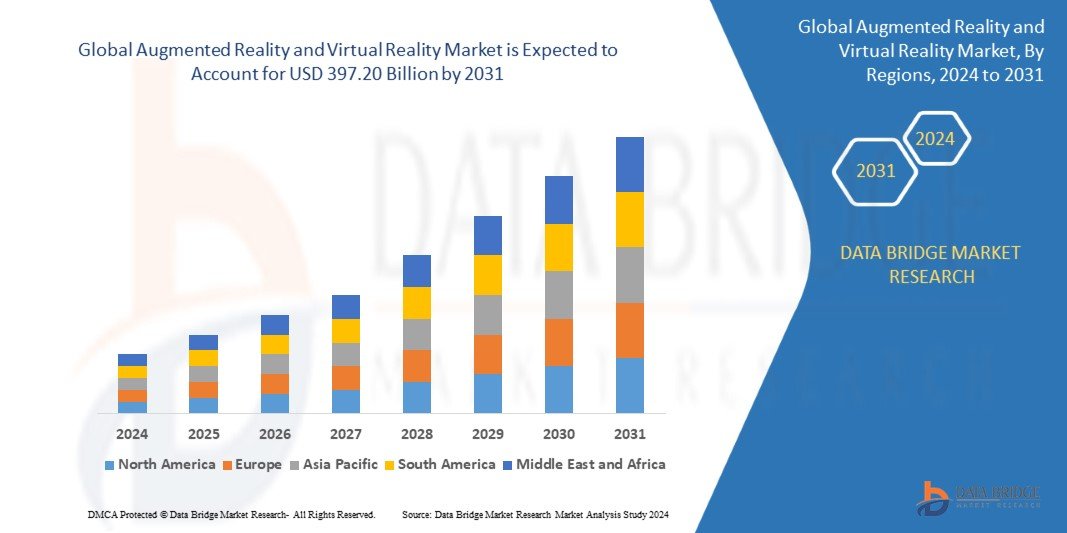
Growth Rate of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Market
The size of the worldwide augmented reality and virtual reality market was estimated at USD 5.97 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 69.00% to reach USD 397.20 billion by 2031.
Conclusion
AR and VR are not only transforming how games are played but also expanding the possibilities for game design and player interaction. As these technologies continue to evolve, the gaming industry will likely see even more innovative and immersive experiences, attracting a diverse audience and setting new standards for entertainment and interactivity.