Varicose veins and spider veins are common vascular conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. While they are typically not dangerous, they can be unsightly and cause discomfort, leading many to seek treatment options. Among the various solutions available, sclerotherapy has become one of the most popular choices due to its effectiveness and minimally invasive nature. However, several other vein treatment methods also exist, each with its own set of benefits. This article will compare sclerotherapy to other common vein treatments, including laser treatments, endovenous laser therapy (EVLT), and vein stripping, to help you make an informed decision about the best approach for your needs.
What Is Sclerotherapy?
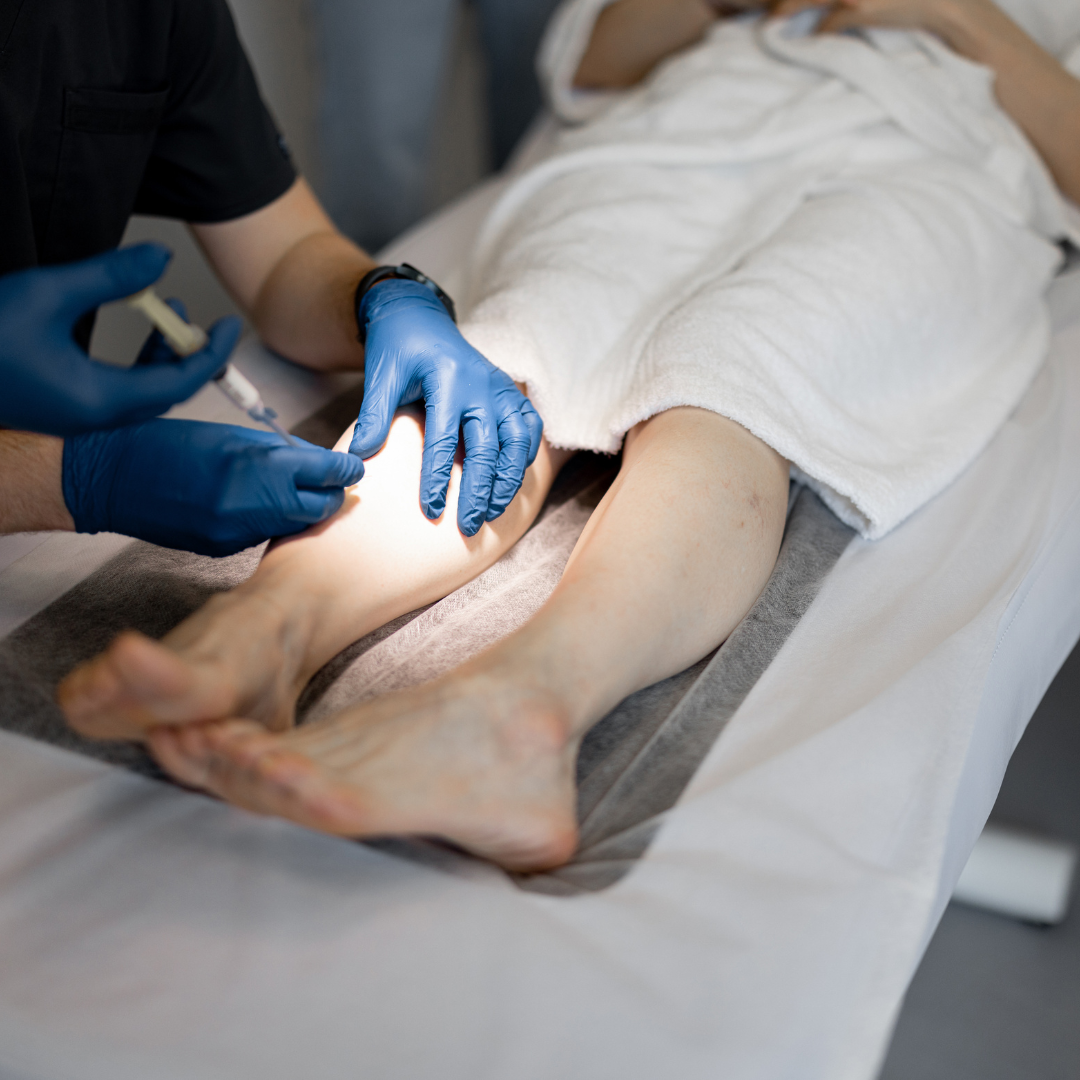
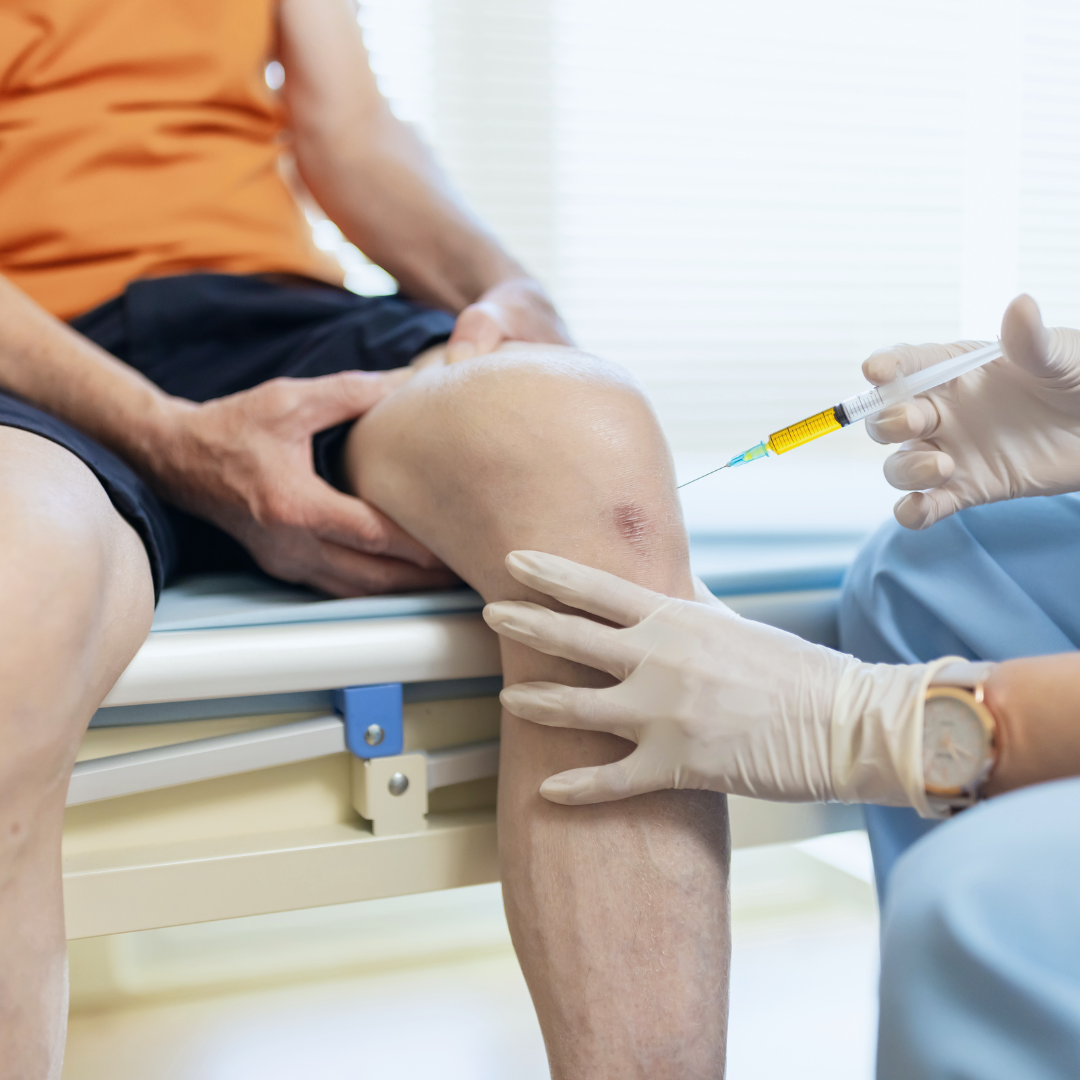
sclerotherapy in Abu Dhabi is a non-surgical procedure used to treat varicose veins and spider veins. The treatment involves injecting a sclerosant solution directly into the affected veins, causing them to collapse and eventually fade from view. The solution irritates the inner lining of the vein, leading to its closure and absorption by the body. Over time, the veins are reabsorbed, and blood is rerouted to healthier veins, improving the appearance of the skin.
Sclerotherapy is most commonly used for smaller veins and spider veins but can also be effective for treating larger varicose veins in certain cases. The procedure is minimally invasive, requires no incisions, and involves very little downtime, making it a preferred option for many patients.
Laser Treatments for Veins
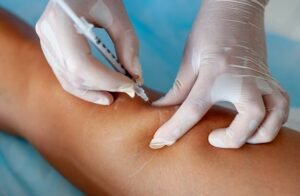
Laser treatments, including both superficial laser therapy and endovenous laser therapy (EVLT), are also widely used for treating varicose veins. Laser vein treatment uses focused light to heat and damage the vein walls, causing the veins to close and eventually be absorbed by the body.
Superficial Laser Therapy
Superficial laser therapy, also known as laser vein removal, is commonly used to treat small, superficial veins, such as spider veins. During the procedure, a laser is passed over the skin, targeting the veins beneath. The heat from the laser damages the blood vessel walls, causing the veins to collapse. The procedure is typically quick, and patients can return to normal activities immediately afterward.
While effective for small veins, superficial laser therapy is not suitable for treating larger varicose veins, as the laser may not penetrate deeply enough to affect the larger vessels.
Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT)
Endovenous laser therapy (EVLT) is a more advanced form of laser treatment used to treat larger varicose veins. In this procedure, a laser fiber is inserted into the vein through a small incision or needle puncture. The laser is then used to heat and seal the vein from the inside out, causing it to collapse and be absorbed by the body. EVLT is typically performed under local anesthesia and requires only small incisions, making it a minimally invasive procedure.
EVLT is effective for treating larger veins and is considered an excellent alternative to vein stripping, which is a more invasive surgical method. However, it may not be suitable for all patients, depending on the severity of their vein condition.
Vein Stripping
Vein stripping is a traditional surgical procedure used to treat varicose veins. The process involves the removal of the affected vein through small incisions made in the skin. The vein is surgically “stripped” out of the body, and blood is rerouted through healthier veins. While vein stripping can be effective, it is a more invasive treatment compared to sclerotherapy or laser treatments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vein Stripping
One of the main advantages of vein stripping is its ability to treat large, extensive varicose veins. However, it comes with several downsides. It requires general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation, and the procedure typically involves a longer recovery time compared to other non-invasive treatments. There is also a higher risk of complications such as infection, scarring, and nerve damage.
Because of these drawbacks, vein stripping is generally considered a last resort for patients who have not had success with less invasive options such as sclerotherapy or laser treatments.
Comparing Sclerotherapy to Other Treatments
Effectiveness
Sclerotherapy is highly effective for treating smaller veins, including spider veins and some varicose veins. For larger veins, however, other treatments like EVLT or vein stripping may be more suitable. Laser treatments, especially EVLT, can be effective for treating larger veins and those deeper in the body. The choice of treatment depends on the size, location, and severity of the veins being treated.
For smaller veins, sclerotherapy is often the first choice due to its proven track record of success. Laser treatments may be used for more significant varicose veins, especially when they are deeper under the skin.
Pain and Discomfort
Sclerotherapy is known for being relatively painless. Most patients experience only slight discomfort during the injection process, and there is little to no downtime afterward. Mild bruising may occur, but it typically fades within a few days.
Laser treatments, including EVLT, are also minimally invasive and typically well-tolerated. Patients may experience some discomfort during the procedure, but the treatment is usually done under local anesthesia, minimizing pain.
Vein stripping, on the other hand, is more invasive and typically requires general anesthesia. As a result, the recovery period is longer, and there may be more discomfort during and after the procedure. Swelling, bruising, and pain are common side effects of vein stripping.
Recovery Time
Sclerotherapy has the shortest recovery time of all the treatments. Most patients can resume normal activities immediately after the procedure. While patients are advised to avoid intense physical activities for a few days, there is no need for extended rest.
Laser treatments, particularly superficial laser therapy, also have minimal downtime. Patients can typically return to work or other normal activities the same day. For EVLT, the recovery period is a bit longer, with most patients taking a few days to a week to fully recover.
Vein stripping has the longest recovery time. Patients can expect to take several weeks off from work or strenuous activities to allow for proper healing. Swelling and bruising may last for weeks, and there may be a risk of developing blood clots or other complications.
Risks and Complications
Sclerotherapy carries minimal risk. Some patients may experience temporary side effects such as bruising, redness, or slight swelling at the injection site. Rarely, blood clots or allergic reactions can occur, but these risks are minimal.
Laser treatments, including EVLT, are generally safe with a low risk of complications. Some patients may experience temporary redness, swelling, or bruising, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days. In rare cases, nerve injury or deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can occur.
Vein stripping carries a higher risk of complications due to its surgical nature. These may include infection, scarring, nerve damage, or blood clots. As a result, vein stripping is generally only recommended for severe cases that do not respond to less invasive treatments.
Conclusion
When it comes to treating varicose veins, sclerotherapy offers a safe, effective, and minimally invasive solution, particularly for smaller veins. Laser treatments, including both superficial laser therapy and EVLT, provide excellent options for larger veins and those deeper beneath the skin. Vein stripping, while effective for severe cases, is an invasive procedure that involves a longer recovery time and more significant risks. Ultimately, the best treatment for you depends on the size, location, and severity of your varicose veins, as well as your personal preferences for pain, recovery time, and potential risks. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment for your needs.