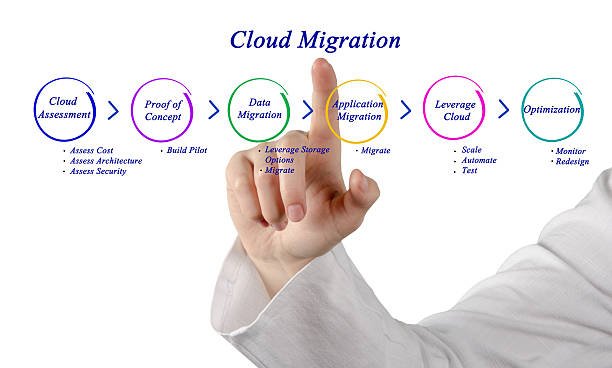
Cloud migration—the process of moving digital assets, services, databases, IT resources, and applications into the cloud—is increasingly becoming a necessity for businesses. A well-structured cloud migration strategy ensures a seamless transition, minimizes risks, and optimizes costs. In this blog, we’ll break down the essential steps to crafting a robust cloud migration strategy that works for businesses of all sizes.
1. Understand the Importance of Cloud Migration
Cloud migration offers numerous benefits, including scalability, cost-efficiency, and enhanced flexibility. By adopting the cloud:
- Businesses can reduce dependency on physical hardware.
- Companies gain access to a wide range of tools and services for innovation.
- Operations can adapt quickly to market changes with minimal disruptions.
However, moving to the cloud without a proper strategy can lead to downtime, security vulnerabilities, or increased costs.
2. Assess Current Infrastructure
Before planning a migration, it’s crucial to evaluate the existing IT infrastructure. Key considerations include:
- Hardware and Software Inventory: Understand what needs to be migrated, retired, or replaced.
- Application Dependencies: Identify interdependent systems to ensure they function correctly after migration.
- Performance Metrics: Assess how existing systems are performing to set benchmarks for cloud services.
This step allows businesses to decide whether a full or partial migration is necessary.
3. Define Business Objectives and Goals
Why is your business moving to the cloud? Common goals include:
- Reducing IT costs.
- Improving operational efficiency.
- Enabling remote work.
- Enhancing data security and disaster recovery capabilities.
Setting clear objectives ensures that the migration aligns with the organization’s long-term goals.
4. Choose the Right Cloud Model
Businesses can choose from various cloud models based on their needs:
- Public Cloud: Services are hosted by third-party providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. Suitable for scalability and cost efficiency.
- Private Cloud: Exclusive use by one organization for greater control and security.
- Hybrid Cloud: A combination of public and private clouds to balance flexibility and security.
- Multi-Cloud: Using multiple providers to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize performance.
Understanding the pros and cons of each model helps in making an informed decision.
5. Develop a Migration Plan
A detailed migration plan acts as a roadmap for the transition. Key steps include:
- Prioritize Workloads: Determine which applications or systems should move first based on criticality.
- Select Migration Tools: Use tools like AWS Migration Hub, Azure Migrate, or third-party platforms for efficiency.
- Test Environments: Create sandbox environments to test the migration process and resolve potential issues.
- Set a Timeline: Establish deadlines to keep the process on track without overwhelming resources.
6. Ensure Data Security and Compliance
Data security is a top concern during migration. To mitigate risks:
- Encrypt data during transit and storage.
- Ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
- Use access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Collaborate with cloud providers to implement shared responsibility for security.
7. Train Your Team
Cloud environments differ from traditional on-premises systems. Conduct training sessions to:
- Help employees understand new tools and workflows.
- Address questions about managing cloud-based resources.
- Empower IT teams to troubleshoot issues effectively.
8. Monitor and Optimize After Migration
Migration isn’t the end—it’s the beginning of leveraging cloud technology. After completing the transition:
- Monitor performance using cloud-native tools like AWS CloudWatch or Azure Monitor.
- Optimize costs by analyzing usage patterns and scaling resources accordingly.
- Regularly review and update the cloud strategy to align with evolving business needs.
Conclusion
A successful cloud migration strategy requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing optimization. By following these steps, businesses can achieve a seamless transition, harness the benefits of the cloud, and stay competitive in a fast-changing digital landscape.
Are you planning a cloud migration? Start by assessing your infrastructure and identifying the best cloud model for your needs!