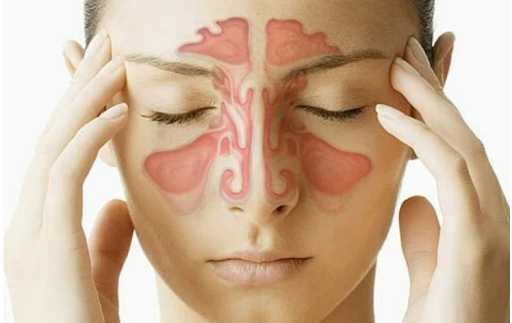
Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, are a common condition affecting millions of people each year. They occur when the sinuses, air-filled cavities around the nose and eyes, become inflamed due to bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Among the antibiotics used to treat bacterial sinus infections, Azithromycin is a widely prescribed and effective option.
Understanding Sinus Infections
Sinus infections can be acute, lasting a few days to weeks, or chronic, lasting for months. Symptoms of sinus infections include:
- Nasal congestion
- Facial pain or pressure
- Thick, discolored nasal discharge
- Postnasal drip
- Loss of smell or taste
- Headaches
- Fever
Acute sinusitis is often caused by a viral infection, such as the common cold, and typically resolves on its own. However, bacterial infections can develop in the sinuses, leading to more severe and prolonged symptoms. In these cases, antibiotics like Azithromycin are often prescribed to eliminate the bacterial infection and alleviate symptoms.
How Azithromycin Works in Sinus Infections
Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic, which works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. It binds to the bacterial ribosome, preventing bacteria from producing the proteins they need to grow and replicate. By stopping bacterial growth, Azithromycin helps the immune system eliminate the infection.
Azithromycin is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis, which are common culprits of bacterial sinus infections.
When Is Azithromycin Prescribed for Sinus Infections?
Azithromycin is typically prescribed for sinus infections in cases where:
- The infection is suspected to be bacterial, and symptoms have lasted for more than 10 days.
- The patient has worsening symptoms after initial improvement, suggesting a secondary bacterial infection.
- The patient is allergic to other antibiotics, such as penicillins (amoxicillin) or cephalosporins.
Azithromycin is often favored due to its broad-spectrum activity and its once-daily dosing, which makes it more convenient for patients.
Dosage and Duration
For the treatment of bacterial sinus infections, Azithromycin is commonly prescribed as follows:
- 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg once daily for the next 4 days (total of a 5-day course).
This shorter duration of treatment is one of Azithromycin’s key advantages compared to other antibiotics that may require a longer course. Buy Azithromycin wholesale online
Benefits of Azithromycin for Sinus Infections
Azithromycin offers several benefits in the treatment of sinus infections:
- Broad-spectrum activity: It targets a wide range of bacteria, including many of the common pathogens responsible for sinus infections.
- Once-daily dosing: This makes it easier for patients to adhere to the treatment regimen, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
- Shorter treatment course: The typical 5-day course is shorter than many other antibiotics, which can improve patient compliance.
- Fewer gastrointestinal side effects: Compared to some other antibiotics, Azithromycin is less likely to cause stomach upset or diarrhea.
Side Effects and Precautions
While Azithromycin is generally well-tolerated, some patients may experience side effects, including:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Dizziness
In rare cases, Azithromycin can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Allergic reactions: Rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Immediate medical attention is required if these occur.
- QT prolongation: Azithromycin may cause a condition that affects the heart’s rhythm, known as QT prolongation. Patients with a history of heart conditions or those taking medications that affect the heart’s rhythm should inform their doctor before starting treatment.
- Liver problems: Rarely, Azithromycin can cause liver damage. Patients should contact their doctor if they notice symptoms like jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), dark urine, or persistent nausea.
Drug Interactions
Azithromycin may interact with other medications, affecting their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Common drug interactions include:
- Antacids: Antacids containing magnesium or aluminum can reduce the absorption of Azithromycin. It is recommended to take Azithromycin at least two hours before or after using such antacids.
- Warfarin: Azithromycin can increase the effects of warfarin, a blood thinner, leading to an increased risk of bleeding.
- Heart medications: Azithromycin can interact with certain heart medications, such as digoxin, increasing the risk of side effects.
It’s important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
Alternatives to Azithromycin
While Azithromycin is an effective treatment for bacterial sinus infections, other antibiotics may also be prescribed based on the patient’s medical history, allergies, or local bacterial resistance patterns. Alternatives include:
- Amoxicillin or Amoxicillin-Clavulanate: These are often first-line treatments for bacterial sinus infections.
- Doxycycline: This antibiotic may be prescribed if the patient is allergic to penicillins.
- Cephalosporins: These are another class of antibiotics used to treat bacterial sinusitis.
Conclusion
Azithromycin is a powerful and convenient antibiotic for the treatment of bacterial sinus infections, especially for patients who may be allergic to other antibiotics or need a shorter course of treatment. While generally well-tolerated, it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and complete the full course of treatment to ensure the infection is fully cleared. As with any medication, patients should be aware of potential side effects and drug interactions, and consult their healthcare provider if any concerns arise.
If you are experiencing symptoms of sinusitis and believe you may need antibiotics, speak with your healthcare provider to determine whether Azithromycin is the right choice for you.