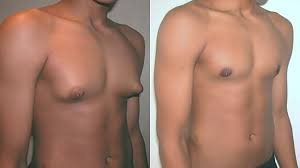
Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in men. While it is a common issue that affects a large percentage of the male population, it can lead to significant psychological distress for many. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for anyone dealing with gynecomastia. In this article, we will explore all aspects of gynecomastia, providing a comprehensive guide to the condition.
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia occurs when the glandular tissue in the male breast grows abnormally, often leading to a noticeable increase in breast size. This condition can affect one or both breasts, and it can occur at various stages of life, including during infancy, puberty, and adulthood.
Types of Gynecomastia
There are three common types of gynecomastia:
- Pubertal Gynecomastia: This is the most common form and affects young boys during puberty. It often resolves on its own within a few months to a couple of years.
- Adult Gynecomastia: This type occurs in adult men and is usually due to hormonal imbalances, medications, or underlying health conditions.
- Pseudo-Gynecomastia: In this case, the enlargement is due to an accumulation of fat rather than glandular tissue, often seen in individuals who are overweight or obese.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia can result from several factors that affect the hormonal balance in the body. The most common cause is an imbalance between estrogen (female hormone) and testosterone (male hormone), where estrogen levels are disproportionately high. Below are some common causes:
1. Hormonal Imbalance
Testosterone plays a crucial role in regulating male characteristics, including breast size. An increase in estrogen levels or a decrease in testosterone levels can lead to the development of gynecomastia. This hormonal imbalance can occur due to:
- Aging: As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, which can lead to an imbalance with estrogen.
- Puberty: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty can trigger temporary gynecomastia in adolescent boys.
- Health Conditions: Disorders affecting hormone production, such as hypogonadism, hyperthyroidism, or tumors, can cause gynecomastia.
2. Medications and Drugs
Certain medications and substances can lead to the development of gynecomastia. Some common culprits include:
- Anti-androgens used to treat prostate conditions
- Anabolic steroids for muscle building
- Certain antidepressants and antipsychotics
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Marijuana use
3. Obesity
Obesity is a significant risk factor for gynecomastia, particularly in cases of pseudo-gynecomastia. Excess fat tissue around the chest can mimic the appearance of enlarged breast tissue.
4. Alcohol and Drug Use
Chronic alcohol consumption and recreational drug use, such as heroin or amphetamines, can also contribute to the development of gynecomastia by affecting the liver’s ability to metabolize estrogen.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
The main symptom of gynecomastia is an enlargement of one or both breasts. Other associated symptoms may include:
- Tenderness or pain in the breast tissue
- Swelling or lumps in the chest area
- Nipple changes such as increased size or sensitivity
In some cases, the condition may resolve on its own, while in others, it may persist and cause significant emotional and physical discomfort.
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia
A proper diagnosis of gynecomastia is essential to differentiate it from other potential conditions that may cause similar symptoms, such as breast cancer in men. To confirm the diagnosis, a healthcare provider will typically:
- Conduct a physical exam to assess the breast tissue and overall health.
- Take a medical history to evaluate potential risk factors, including medications, lifestyle, and family history.
- Order blood tests to check hormone levels and identify any underlying conditions.
- Perform imaging tests such as ultrasound or mammography if there is a need to rule out other conditions like tumors or cysts.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
Treatment for gynecomastia depends on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s overall health and preferences. Here are some of the most common treatment options:
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
- Medications: In some cases, medications like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) or aromatase inhibitors can help correct the hormonal imbalance and reduce breast tissue growth.
- Weight Management: For cases of pseudo-gynecomastia, losing excess weight through a balanced diet and exercise may help reduce the appearance of enlarged breasts.
- Avoiding Drug Use: Discontinuing drugs or medications that may be contributing to gynecomastia can result in improvement over time.
2. Surgical Treatment
When non-surgical treatments are ineffective or if the gynecomastia is causing significant distress, surgery may be recommended. There are two main surgical options:
- Liposuction: This technique removes excess fat tissue through small incisions, making it an ideal option for individuals with pseudo-gynecomastia.
- Mastectomy: For individuals with glandular tissue growth, a mastectomy involves the removal of the excess glandular tissue, creating a flatter, more masculine chest contour.
Surgical procedures are generally safe, and most patients report high levels of satisfaction with the results. However, as with any surgery, there are risks involved, such as infection, scarring, and asymmetry.
Psychological Impact of Gynecomastia
The psychological effects of gynecomastia should not be underestimated. Many men feel self-conscious about their appearance, leading to anxiety, depression, and a lack of self-esteem. The condition can also affect relationships and social interactions, as individuals may avoid situations where they need to remove their shirts, such as swimming or exercising.
Seeking counseling or joining support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of living with gynecomastia. For some, treatment options like surgery or medication can help restore confidence.
Prevention of Gynecomastia
While some causes of gynecomastia, such as puberty or aging, are unavoidable, there are steps that men can take to reduce their risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise to reduce the risk of obesity-related gynecomastia.
- Avoid alcohol and drug abuse to prevent gynecomastia caused by substance use.
- Discuss medications with a healthcare provider, especially if taking drugs that may influence hormone levels.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia is a common yet often misunderstood condition that can affect men of all ages. Although it can be caused by various factors, it is generally treatable, with options ranging from medication to surgery. If you or someone you know is struggling with gynecomastia, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment and address any emotional concerns. With the right support, individuals with gynecomastia can regain their confidence and lead a healthy, fulfilling life.